반응형
토마토마토마토
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/7576

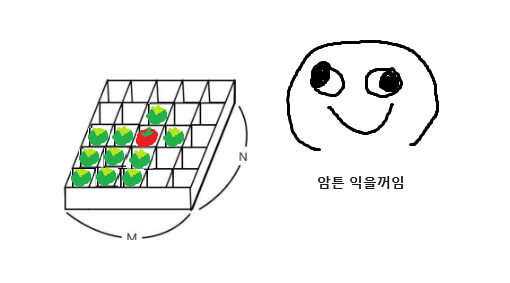
익지 않은 토마토는 근처 토마토를 익게 하는 문제
혼자 익는경우가 없을때
모든 토마토가 익을때까지 최소일수 를 구하는 문제
간단하게 BFS 를 써서 푸는 문제다
골드 5인만큼 그냥 시뮬레이션 돌리면 풀린다.
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include <tuple>
using namespace std;
#define XYZ tuple<int,int>
vector<XYZ> nonfire;
const XYZ MoverDirection[4] = { {1,0} ,{-1,0} ,{0,-1} ,{0,1} };
vector<vector<int>> vec;
int N = 0, H = 0;
///토마토 익는칸 확인 함수
vector<XYZ> findNextTomato(vector<XYZ> _xyz) {
vector<XYZ> firebe = {};
for (auto a : _xyz) {
for (auto Dir : MoverDirection) {
int xyz2[2] = { get<0>(a) + get<0>(Dir),get<1>(a) + get<1>(Dir) };
if (!(get<0>(a) + get<0>(Dir) < N && get<0>(a) + get<0>(Dir) >= 0 &&
get<1>(a) + get<1>(Dir) < H && get<1>(a) + get<1>(Dir) >= 0)) {
continue;
}
if (vec[xyz2[0]][xyz2[1]] == 0) {
firebe.push_back(XYZ(xyz2[0], xyz2[1]));
vec[xyz2[0]][xyz2[1]] = 1;
}
}
}
//익은것들 위치반환
return firebe;
}
int main() {
cin >> H >> N ;
vector<XYZ> fire;
int answer = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
vec.push_back({});
for (int j = 0; j < H; j++)
{
int a;
cin >> a;
vec[i].push_back(a);
if (a == 1)
{
fire.push_back(XYZ(i, j));
}
if (a == 0) {
nonfire.push_back(XYZ(i, j));
}
}
}
while (true)
{
if (fire.size() <= 0)
break;
//다음으로 익을 토마토 구하기
fire = findNextTomato(fire);
//일자 업데이트
answer++;
}
for (auto a : nonfire) {
if (vec[get<0>(a)][get<1>(a)] == 0)answer = 0;
}
cout << (answer - 1);
}
익은 위치와 익지않은 위치를 받아준뒤
}
while{
func (익은 토마토들)
return이제 익은 토마토 위치 반환
반복하며 answer+1
}
}
위와 같은 행위를 결국 익을게 없을때 까지 반복한다.
더이상 익을게 없을때
안익었던 토마토들이 아직도 익지않았는지 확인한다.
매우 쉬운코드
예전에 짠코드여서 왜 그랬는지 모르겠지만 queue를 써봤다가 안쓰고 vector로 풀어보려고 풀어보았던거 같다.
queue로 BFS를 풀고 얕은복사를 좀더 활용하는게 좋을거같다.
만약 시각적으로 보면서 확인해야 이해하기 쉬울거 같다 생각한다면!
while (true)
{
if (fire.size() <= 0)
break;
fire = findNextTomato(fire);
//cout << endl;
for (auto x : vec) {
for (auto y : x) {
cout << y;
cout << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
answer++;
}
를 추가해서 점점 퍼지는걸 볼수있따 :-)